Which of the statements about B2B e-commerce is correct?
In the dynamic landscape of business interactions, B2B e-commerce, denoting the online exchange of goods, services, or information between businesses, has emerged as a pivotal force driving economic transactions. Amidst the intricate web of complexities inherent in this digital realm, a fundamental question surfaces: “Which of the statements about B2B e-commerce is correct?” This inquiry serves as the guiding beacon for our exploration into the nuances of B2B transactions. As we embark on this journey, our aim is to scrutinize, dissect, and demystify the statements surrounding B2B e-commerce, unraveling the truths that shape the landscape of this evolving phenomenon. Join us in this intellectual expedition as we navigate through the intricacies of B2B e-commerce, seeking clarity and understanding amidst the diverse assertions that surround it.
Statement 1: The transactions involve review by a team of people before making a purchase decision
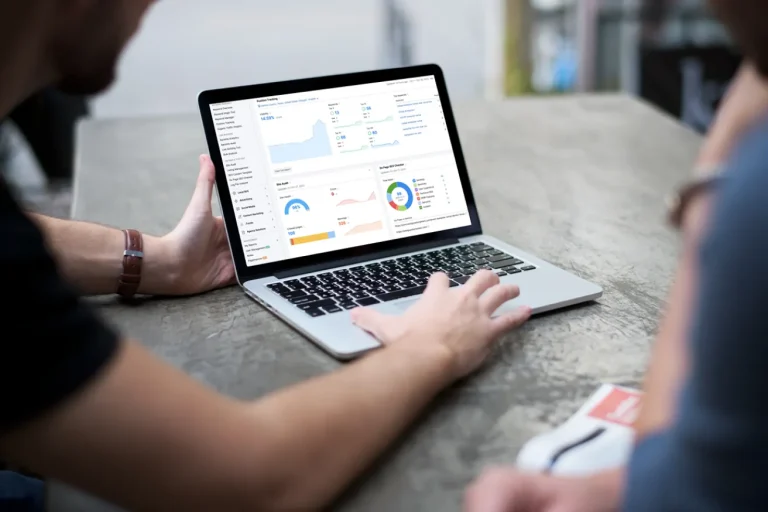
Indeed, this statement holds true. B2B purchases, characterized by their complexity and often substantial costs, necessitate the scrutiny and approval of multiple stakeholders. Unlike the more impulsive and individual nature of B2C transactions, B2B acquisitions demand a rational, strategic, and collective approach. A case in point is a manufacturing company contemplating the acquisition of a new machine; such decisions require consultations with engineers, managers, accountants, and suppliers. B2B buyers extensively utilize online platforms for research, product comparisons, and evaluations, leveraging various sources like websites, social media, blogs, forums, and online communities. Additionally, communication and negotiation tools such as email, chat, video conferencing, and online auctions play pivotal roles in facilitating these intricate transactions.

Statement 2: The end consumer is the decision-maker in the transactions
Contrary to this statement, B2B buyers do not serve as the ultimate decision-makers. Instead, they function as intermediaries, acquiring products or services with the intention of reselling or incorporating them into their own operational processes. Consider a wholesaler purchasing clothing from a manufacturer; the wholesaler does not wear the clothing but sells it to retailers, who subsequently cater to end consumers. Similarly, a hospital obtaining medical equipment from a supplier doesn’t use the equipment directly but provides it to healthcare professionals and patients. This distinction in roles translates into different needs, preferences, and evaluation criteria for B2B buyers, focusing on aspects such as quality, reliability, durability, and compatibility.
Statement 3: B2B websites offer fixed, consistent pricing for all purchases
This statement proves incorrect, as B2B pricing exhibits dynamic, variable, and negotiable characteristics. Unlike the transparent, standardized pricing often associated with B2C transactions, B2B pricing operates in a more opaque and customizable realm. The dynamics of B2B pricing hinge on factors like transaction volume, frequency, and the relational context between buyer and seller. Consequently, engaging in activities such as price discovery, bargaining, and haggling becomes integral to arriving at mutually acceptable agreements. Sellers employ online tools to tailor pricing, discounts, and incentives based on individual buyer profiles and behaviors, including loyalty programs, volume discounts, and dynamic pricing strategies.

Statement 4: Shopping websites use B2B e-commerce
This statement is unfounded, as shopping websites predominantly exemplify B2C e-commerce, geared towards transactions between businesses and end consumers. Popular platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba facilitate consumer access to products from businesses or other consumers. The design, functionality, and marketing strategies of shopping websites markedly differ from their B2B counterparts. Shopping websites prioritize user-friendly interfaces, attractive designs, and engaging features such as product reviews, ratings, recommendations, and wish lists. In contrast, B2B websites prioritize professionalism, informativeness, and efficiency, offering features like product specifications, comparisons, quotations, and order processing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, B2B e-commerce emerges as a multifaceted realm with statement 1 standing as the only accurate assertion among the four. Successful navigation of the intricacies inherent in B2B transactions requires adherence to best practices, utilization of reliable platforms, and the cultivation of trust and loyalty.
Onextdigital excels in delivering premier Web Development Services, backed by a decade of expertise. For further details, contact us without delay!